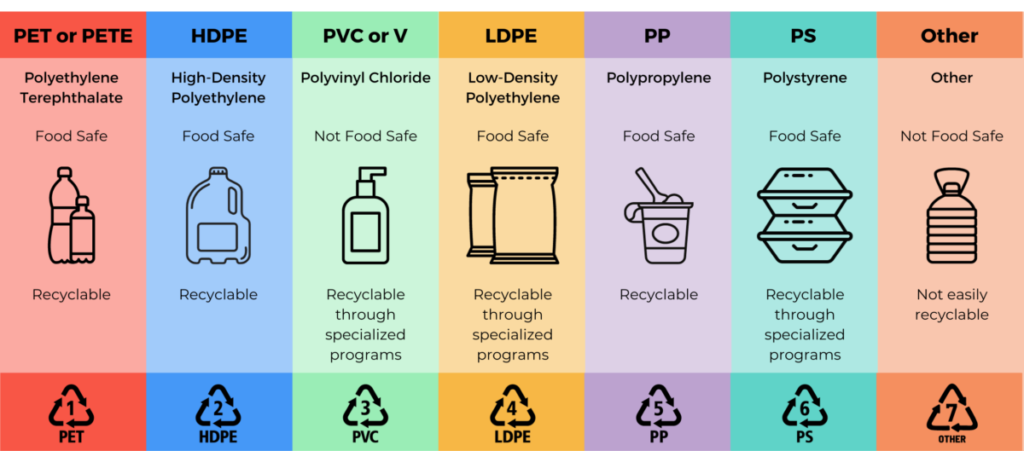
In a time where maintainability is a higher priority than any time in recent memory, many are searching for ways of decreasing their natural effect by pursuing more brilliant decisions in the kitchen. A significant supporter of plastic waste is the utilization of expendable or plastic-based kitchen instruments. From utensils to cutting sheets and sifters, there are eco accommodating choices that are similarly compelling and frequently longer enduring. Here is a breakdown of the best options in contrast to normal plastic kitchen basics.
1. Options in contrast to Plastic Utensils
Plastic utensils have turned into a typical component in numerous families, yet their single-use nature makes them a serious ecological concern. Luckily, there are a few eco-accommodating options that can be reused endlessly time once more.
Wooden Utensils
Wooden utensils are an immortal option in contrast to plastic. Produced using maintainable materials like bamboo or beechwood, wooden spoons, forks, and spatulas are normally solid and biodegradable. They’re ideally suited for non stick cookware as they won’t scratch surfaces. Bamboo, specifically, is a quickly inexhaustible asset, which makes it a much more eco-accommodating choice.
Hardened Steel Utensils
Hardened steel is an enduring, non-harmful, and completely recyclable material. Hardened steel utensils can endure high temperatures, making them ideal for cooking. Not at all like plastic, they will not corrupt or filter unsafe synthetic substances into your food. Also, putting resources into excellent tempered steel utensils can set aside your cash over the long haul as they won’t break or twist without any problem.
Biodegradable and Compostable Utensils
For those searching for single-use choices, biodegradable and compostable utensils produced using plant-based materials like cornstarch, sugarcane, or palm leaves are extraordinary choices. These utensils are intended to separate in fertilizing the soil conditions, diminishing waste that would somehow wind up in landfills.
2. Options in contrast to Plastic Cutting Sheets
Cutting sheets are fundamental kitchen apparatuses, yet plastic cutting sheets can hold onto microbes and break down rapidly. There are various manageable options that are both protected and strong.
Bamboo Cutting Sheets
Bamboo is one of the most incredible options in contrast to plastic cutting sheets. An exceptionally sustainable asset develops quickly without the requirement for composts or pesticides. Bamboo cutting sheets are normally antimicrobial, and that implies they’re less inclined to assimilate microbes and scents contrasted with plastic sheets. They are solid, delicate on blades, and come in different shapes and sizes to suit different cooking needs.
Wooden Cutting Sheets
Wooden cutting sheets produced using hardwoods like maple, pecan, or cherry are another extraordinary choice. In addition to the fact that they look lovely in the kitchen, but on the other hand they’re durable and enduring. Wood cutting sheets are delicate on blade edges, safeguarding their sharpness. When kept up appropriately with ordinary oiling, these sheets can keep going for a long time, diminishing waste and the requirement for substitutions.
Glass Cutting Sheets
However, more uncommon, glass cutting sheets offer an eco-accommodating and simple to clean other option. They are non-permeable, so they don’t retain smells or microorganisms, and they can be disinfected in a dishwasher. Glass is additionally exceptionally tough, however it tends to be challenging for blade edges, so it’s best utilized for undertakings like cutting leafy foods instead of hacking thick fixings like meat.
3. Options in contrast to Plastic Sifters
Plastic sifters are much of the time utilized for depleting pasta or washing vegetables, however there are numerous economical choices that work similarly also without adding to plastic waste.
Hardened Steel Sifters
A hardened steel sifter is a sturdy, durable elective that can be utilized for a wide range of food readiness. They come in different cross section sizes, making them flexible for stressing fluids, filtering dry fixings, or washing produce. Treated steel is impervious to rust, and not at all like plastic, it won’t twist or debase after some time.
Bamboo Sifters
For a more provincial, yet reasonable choice, bamboo sifters are an extraordinary decision. Lightweight and tough, bamboo sifters are great for washing vegetables or stressing fragile fixings like rice. Bamboo additionally has regular antimicrobial properties, so you can be certain that your sifter is clean and safe for food use.
Network Material Sifters
Network material sifters are one more option in contrast to plastic sifters. These texture sifters are frequently produced using cotton, material, or other regular filaments. They are perfect for stressing fluids lie stocks or making nut milk. The texture can be effortlessly washed and reused, making it a feasible choice for the eco-cognizant cook.
Conclusion
Changing to options in contrast to plastic utensils, cutting sheets, and sifters is a little change that can immensely affect the climate. Whether we are picking bamboo, wood, treated steel, or texture based items, there are reasonable choices accessible to supplant plastic in our kitchen. By making these basic switches, we are lessening plastic waste as well as putting resources into durable, eco-accommodating options that will serve us long into the future. Doing the change to reasonable kitchen apparatuses doesn’t simply help the planet, it likewise improves our cooking experience.